The transition toward electric mobility has reached a fever pitch as we move through 2026. With major automakers having phased out several internal combustion models and the infrastructure for charging reaching a state of maturity, the focus for most homeowners has shifted from “if” they should install a home charger to “how” they can do it most efficiently. This guide serves as the definitive resource for navigating the complex landscape of residential energy technology, electrical codes, and financial incentives available today.
- Understanding the EV Charging Landscape in 2026
- The Financial Landscape: Incentives and Cost Breakdowns
- Technical Requirements and Electrical Infrastructure
- Step-by-Step Installation Guide for 2026
- Critical Updates in the 2026 National Electrical Code (NEC)
- Integrating Renewable Energy: Solar and Storage
- Daily Maintenance and Long-Term Care
- Conclusion and Strategic Takeaways
The year 2026 represents a unique crossroads. We are seeing the widespread adoption of the North American Charging Standard (NACS), the rise of bidirectional charging that allows your car to power your house, and a strict deadline for federal tax incentives that every homeowner needs to know. Whether you are a first-time electric vehicle owner or looking to upgrade an existing setup to accommodate the latest tech, the following sections provide a comprehensive roadmap for your installation journey.
Understanding the EV Charging Landscape in 2026
To make an informed decision, you must first understand the current hardware standards. By 2026, the industry has largely consolidated around specific technologies that prioritize speed, safety, and home integration.
The Shift to NACS
The North American Charging Standard, once exclusive to Tesla, is now the primary connector for nearly all new electric vehicles sold in North America. When selecting a home charger in 2026, choosing a NACS-compatible unit ensures that you will not need cumbersome adapters for your vehicle. Even for owners of older vehicles using the CCS or J1772 standards, modern universal chargers now offer integrated dual-head cables to bridge the gap.
The Rise of Bidirectional Charging (V2H and V2G)
One of the most significant advancements available to homeowners this year is bidirectional charging. This technology, often referred to as Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) or Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G), transforms your car from a simple consumer of energy into a massive home battery. In 2026, systems from manufacturers like Enphase, SolarEdge, and General Motors have made it possible to use your EV to provide backup power during grid outages or to lower your utility bills by discharging stored energy during peak pricing hours.
Smart Energy Management Systems
Modern chargers are no longer just “dumb” plugs. They are now central components of a Home Energy Management System (HEMS). These smart units use artificial intelligence to analyze your driving patterns, solar production, and utility rates to determine the most cost-effective time to charge. In 2026, interoperability protocols like Matter and Thread have made it easier for your charger to communicate with your smart thermostat, solar inverter, and home battery.
The Financial Landscape: Incentives and Cost Breakdowns
Investing in a home charging station is a significant financial decision. Understanding the costs and the expiring incentives is crucial for maximizing your return on investment.
The June 30 Deadline for Federal Tax Credits
Perhaps the most critical piece of information for 2026 is the expiration of the Alternative Fuel Vehicle Refueling Property Tax Credit, also known as Section 30C. Under current legislation, qualifying residential installations can receive a tax credit of 30 percent of the total cost, capped at 1,000 dollars. However, this incentive is scheduled to expire on June 30, 2026. To qualify, your system must be fully operational and placed in service before this date.
It is also important to note that eligibility for this credit is now tied to specific census tracts, primarily targeting low-income and non-urban areas. You should consult the latest IRS guidance or a tax professional to confirm your property qualifies before proceeding.
Average Installation Costs in 2026
While technology has improved, costs have stabilized due to increased competition and standardized installation practices. Below is a typical breakdown of what you can expect to pay:
- Standard Level 2 Charger Hardware: 450 to 900 dollars.
- Bidirectional Charging Hardware: 4,000 to 7,500 dollars.
- Electrical Labor and Materials: 600 to 1,800 dollars.
- Permits and Inspections: 100 to 350 dollars.
- Main Panel Upgrade (if required): 1,500 to 3,000 dollars.
Most homeowners find that a standard Level 2 installation costs between 1,200 and 2,500 dollars total. If you are opting for a full V2H backup system, the costs can exceed 10,000 dollars due to the need for specialized transfer switches and power conversion equipment.
Technical Requirements and Electrical Infrastructure
Before you purchase equipment, your home’s electrical system must be evaluated. The demands of a high-power EV charger are significant and require careful planning.
Assessing Your Electrical Panel
The majority of modern Level 2 chargers require a dedicated 240-volt circuit, similar to what a clothes dryer or electric oven uses. Most chargers operate at 32 to 48 amps, requiring a 40 to 60 amp circuit breaker.
In 2026, many homes still have 100-amp service panels. If your panel is already crowded with other heavy loads like air conditioning and electric water heaters, you may not have enough “headroom” for a charger. An electrician will perform a load calculation to determine if your panel can handle the addition. If not, you may need a panel upgrade or a smart load management device.
Smart Load Management Solutions
If a full panel upgrade is too expensive, 2026 technology offers a clever workaround: Power Control Systems (PCS). These devices monitor your home’s total electricity usage in real-time. If you turn on your oven and AC at the same time, the PCS will temporarily throttle the power going to your EV charger to prevent a circuit breaker from tripping. This allows you to install a high-speed charger on an existing panel that would otherwise be considered maxed out.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide for 2026
Following a structured process ensures that your installation is safe, legal, and eligible for all available financial benefits.
Step 1: Conduct a Site Assessment
Start by determining where you want to mount the charger. Most owners prefer the garage, but outdoor installations are increasingly common. Ensure the location is within reach of your vehicle’s charging port, keeping in mind that most charging cables are 18 to 25 feet long. Check for Wi-Fi signal strength at the mounting location, as smart chargers require a stable connection for firmware updates and app control.
Step 2: Choose Your Hardware
Decide between a “plug-in” or “hardwired” unit. While plug-in models (using a NEMA 14-50 outlet) were popular in the past, the 2026 National Electrical Code (NEC) has moved toward favoring hardwired installations for higher power levels and improved safety. Hardwiring also allows for higher charging speeds, often up to 11.5 kilowatts (48 amps), compared to the 9.6 kilowatts (40 amps) typical of plug-in models.
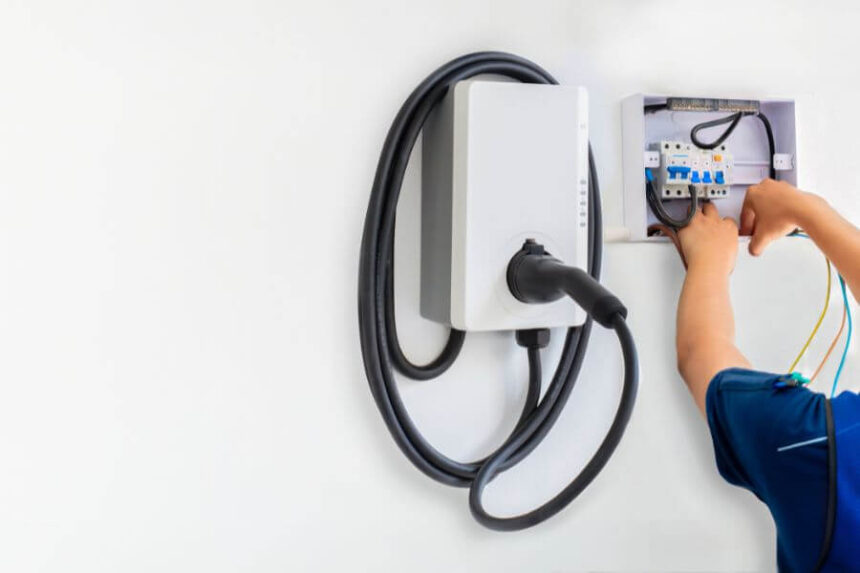
Step 3: Hire a Qualified Professional
The 2026 NEC updates have introduced stricter requirements for who can install EV charging equipment. Many jurisdictions now explicitly require a “qualified person,” which usually translates to a licensed and insured electrician. This shift is designed to prevent fires and electrical failures caused by improper DIY installations. Hiring a pro also ensures that the necessary permits are pulled and inspections are passed.
Step 4: Permitting and Local Approval
Never skip the permitting process. A permit is your proof that the installation meets local safety codes. In many regions, your utility company may also require notification of the new load on the grid. Some utilities even offer discounted “time-of-use” rates specifically for EV owners, but they often require proof of a permitted installation to enroll.
Step 5: Final Testing and Integration
Once installed, your electrician will test the unit to ensure the grounding is correct and the GFCI protection is functioning. After the physical installation is complete, you will need to set up the manufacturer’s app. This is where you will configure your charging schedule to take advantage of off-peak electricity rates.
Critical Updates in the 2026 National Electrical Code (NEC)
Staying compliant with the latest electrical codes is vital for your home’s safety and insurance coverage. The 2026 edition of the NEC includes several major changes.
The Mandatory GFCI Requirement
One of the most discussed changes in the 2026 code is the requirement for Ground-Fault Circuit-Interrupter (GFCI) protection on all EV charging circuits, particularly those using receptacles. While this increases safety, it has led to “nuisance tripping” in some older charger models. Ensure that the hardware you purchase in 2026 is specifically rated to be compatible with the latest GFCI standards to avoid interrupted charging sessions.
Hardwired Requirements for High-Power Units
The new code emphasizes that any charging equipment capable of delivering more than 40 amps of continuous current must be hardwired. This eliminates the use of heavy-duty plugs for the fastest home chargers, reducing the risk of heat buildup at the outlet connection.
Labeling and Emergency Disconnects
For outdoor installations, the 2026 code now requires clearly marked emergency disconnects. This is to assist first responders in quickly de-energizing the system in the event of a fire or other emergency. Your installer must ensure that all labeling meets the new high-visibility standards.
Integrating Renewable Energy: Solar and Storage
By 2026, the synergy between EVs and residential solar power has become seamless. If you have solar panels, or are considering them, your EV charger installation should be part of a larger energy strategy.
Solar-Optimized Charging
Modern smart chargers can be set to “Excess Solar Mode.” In this configuration, the charger communicates with your solar inverter and only charges your car when your panels are producing more electricity than your house is using. This effectively allows you to drive on 100 percent clean, “free” energy generated right on your roof.
Using the EV as a Whole-Home Battery
With the bidirectional capabilities mentioned earlier, your EV can act as a buffer for your solar system. During the day, the car soaks up extra solar energy. At night, the car can feed that power back into your home, reducing your reliance on the grid and further lowering your utility bills. This setup is increasingly seen as a more cost-effective alternative to buying a dedicated stationary wall battery.
Daily Maintenance and Long-Term Care
While EV chargers are generally low-maintenance, a few simple habits will extend the life of your equipment.
Cable Management
The most common point of failure is the charging cable itself. Avoid leaving the cable on the ground where it can be stepped on or driven over. Use the integrated holster or a dedicated wall hook to keep the connector clean and dry. In 2026, many chargers come with “liquid-cooled” or high-durability cables designed for extreme weather, but they still benefit from proper storage.
Firmware Updates
Just like your smartphone, your 2026 smart charger will receive regular software updates. These updates can improve charging efficiency, add new features, and patch security vulnerabilities. Ensure your charger remains connected to your home Wi-Fi to receive these updates automatically.
Inspecting Connections
Every six months, perform a visual inspection of your charger and its connection point. Look for any signs of discoloration or heat damage on the wires or the casing. If you notice a “burning” smell or if the unit feels excessively hot to the touch during operation, shut off the breaker and call your electrician immediately.
Conclusion and Strategic Takeaways
The landscape of home EV charging in 2026 is more advanced and more integrated than ever before. However, the complexity of new codes and the ticking clock on federal incentives mean that proactive planning is essential.
The most important step you can take today is to verify your eligibility for the federal tax credit before the June 30 deadline. Following that, choosing a NACS-compatible, smart-enabled, and potentially bidirectional charger will ensure that your home remains at the cutting edge of energy technology for years to come.
By focusing on professional installation and smart energy management, you are not just installing a car charger. You are building the foundation for a more resilient, cost-effective, and sustainable home energy ecosystem.