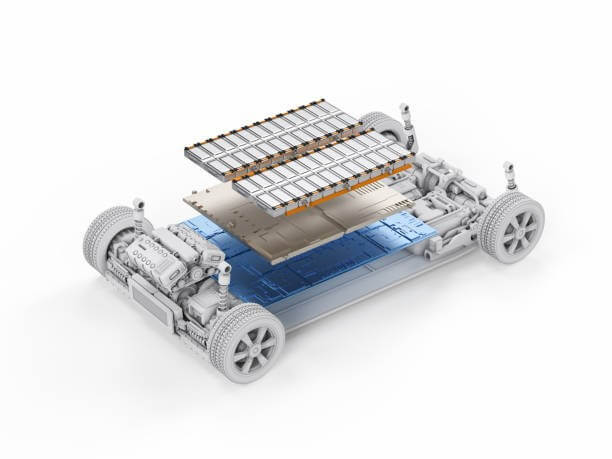
The electric vehicle landscape in 2026 has transformed significantly compared to just a few years ago. With the introduction of solid state batteries, 800 volt architectures, and AI driven management systems, the way we maintain our vehicles has evolved. If you are a new owner of a 2026 model or looking to preserve a legacy lithium ion pack, understanding these changes is vital for maximizing your vehicle’s lifespan and resale value.
- Understanding the 2026 Battery Landscape
- Mastering the State of Charge or SoC
- Smart Charging and 800 Volt Architectures
- Thermal Management: The Silent Battery Killer
- The Role of AI and Software Defined Vehicles
- Driving Habits for Maximum Longevity
- Bidirectional Charging: V2G and V2H
- Maintenance and Diagnostic Tools
- Seasonal Storage Tips
- Summary of 2026 Best Practices
Understanding the 2026 Battery Landscape
As we move through 2026, the diversity in battery chemistry has reached an all time high. It is no longer enough to follow a single set of rules for every electric car. Different chemistries require unique care protocols.
Nickel Cobalt Manganese or NCM Batteries
Most performance focused electric cars in 2026 still rely on NCM chemistry. These batteries offer high energy density and are found in long range versions of popular models. However, they are also the most sensitive to high states of charge and extreme heat. To extend the life of an NCM pack, avoiding the 100 percent charge mark for daily use remains the most critical rule.
Lithium Iron Phosphate or LFP Batteries
LFP batteries have become the standard for entry level and mid range vehicles due to their durability and lower cost. Unlike NCM packs, LFP batteries are much more robust. In fact, many manufacturers now recommend charging LFP packs to 100 percent at least once a week to calibrate the battery management system. This helps the car accurately estimate remaining range and prevents cell imbalance.
The Arrival of Solid State Batteries
2026 marks the early commercial rollout of solid state batteries in high end luxury models and concept test fleets. These batteries replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid ceramic or polymer material. This innovation significantly reduces fire risk and allows for much faster charging speeds without the typical degradation associated with heat. If you are one of the early adopters of this technology, your maintenance routine will be significantly lighter, though thermal stability during ultra fast charging is still a factor to watch.
Mastering the State of Charge or SoC
The most impactful factor in battery longevity is how you manage the State of Charge. In 2026, the “Golden Zone” for lithium ion batteries is widely recognized as being between 20 percent and 80 percent.
The Science of the 80 Percent Limit
When a battery is pushed to its maximum capacity, the internal voltage increases, causing mechanical stress on the cathode and anode. This leads to the formation of microscopic cracks and the growth of the Solid Electrolyte Interphase or SEI layer. By limiting your daily charge to 80 percent, you effectively double the cycle life of the battery. Most 2026 models, including those from Tesla, BMW, and Rivian, allow you to set this limit directly through an app or the dashboard.
Avoiding the Deep Discharge Trap
Just as overcharging is harmful, letting your battery drop below 10 percent can be equally damaging. Modern Battery Management Systems or BMS include “buffers” that prevent the battery from truly reaching zero, but repeatedly hitting these low levels can cause copper shunts to form, which may eventually lead to internal short circuits. In 2026, experts recommend plugging in as soon as the battery hits 20 percent to ensure long term stability.
Smart Charging and 800 Volt Architectures
The charging infrastructure of 2026 is faster than ever. With the expansion of 350kW and even 400kW ultra fast chargers, it is tempting to use them for every top up. However, the speed of electrons moving into the battery generates significant heat.
The Impact of Ultra Fast DC Charging
While 2026 models like the BMW iX3 and the updated Hyundai Ioniq series are designed for 800V charging, frequent use of DC fast charging still accelerates degradation. Research indicates that vehicles relying exclusively on rapid chargers see up to 20 percent more capacity loss over five years compared to those using Level 2 AC home chargers. The best practice remains using slow AC charging for 90 percent of your needs and reserving the ultra fast chargers for long distance road trips.
Megawatt Charging for Heavy Vehicles
For the growing number of electric trucks and SUVs in 2026, Megawatt Charging Systems or MCS have become a reality. These systems deliver massive amounts of power. If your vehicle supports this, ensuring that the battery is preconditioned before the session is the only way to prevent rapid “aging” of the cells.
Thermal Management: The Silent Battery Killer
Temperature is the single biggest external threat to your EV’s health. In 2026, we have seen major breakthroughs in how cars handle this, but the owner still plays a role.
Combating Heat in the Summer
Extreme heat accelerates the chemical reactions within the battery, leading to faster degradation of the electrolyte. In 2026, many manufacturers have adopted immersion cooling, where cells are directly submerged in a non conductive cooling fluid. Even with this tech, parking in the shade or in a garage during peak summer hours is highly recommended. If you must park in the sun, leave the car plugged in so the thermal management system can draw power from the grid instead of the battery to keep the cells cool.
Managing Cold Weather in 2026
Cold temperatures do not necessarily damage the battery permanently, but they do reduce its efficiency. In 2026, most EVs come standard with heat pumps that are 300 percent more efficient than old resistive heaters. To protect the battery in winter, use the “Preconditioning” feature. This warms the battery to its optimal operating temperature (usually around 23 degrees Celsius) while the car is still connected to the charger. This ensures you start your drive with a warm, efficient pack and reduces the strain on the cells during initial acceleration.
The Role of AI and Software Defined Vehicles
In 2026, your car is essentially a computer on wheels. Software updates are no longer just for infotainment; they are critical for battery health.
AI Driven Battery Management Systems
Companies like Bosch and Microsoft have introduced AI platforms that learn your driving habits. These systems can predict when a cell is about to fail or when the pack is overheating before it happens. By analyzing thousands of data points every second, these AI managers adjust the charging curve in real time to minimize stress. Always ensure your vehicle’s software is up to date to benefit from the latest efficiency algorithms.
Predictive Maintenance Alerts
Modern EVs now provide detailed health reports directly to your smartphone. Instead of guessing your battery’s condition, you can see the State of Health or SOH percentage. In 2026, a healthy battery should retain 95 percent of its capacity after the first year and settle into a degradation rate of about 1.5 percent per year. If you see a sudden drop, use your app to schedule a diagnostic check immediately.
Driving Habits for Maximum Longevity
How you drive in 2026 still impacts how long your battery lasts. High performance EVs offer incredible acceleration, but using it constantly comes at a cost.
The Power of Regenerative Braking
One pedal driving has become the standard in 2026. This system uses the electric motor as a generator to slow the car down, sending energy back into the battery. Not only does this extend your range, but it also reduces the heat generated by mechanical brakes. For the best battery health, set your regenerative braking to a moderate level that allows for smooth energy recapture without creating massive current spikes.
Eco Mode and Efficiency
Most 2026 electric cars feature an “Eco” or “Long Range” mode. This setting dampens throttle response and optimizes climate control. By reducing the peak current draw from the battery during acceleration, you reduce the “internal resistance” heat that contributes to long term wear.
Bidirectional Charging: V2G and V2H
One of the biggest trends in 2026 is Vehicle to Grid or V2G and Vehicle to Home or V2H technology. This allows your car to power your house or sell electricity back to the utility company.
Balancing Convenience and Degradation
While V2G is great for sustainability, it does add extra cycles to your battery. Each time you discharge your car to power your home, you are using a portion of the battery’s finite life. To mitigate this, many 2026 home chargers allow you to set a “floor” limit. For example, you can tell the system never to let the car drop below 50 percent while powering the house. This ensures you always have enough range for an emergency while minimizing deep discharge cycles.
Maintenance and Diagnostic Tools
Even in 2026, some physical maintenance is required to keep the electrical system running perfectly.
The Importance of Tire Pressure
It might seem unrelated, but low tire pressure increases rolling resistance. This forces the motor to draw more current from the battery to maintain speed, leading to faster depletion and more frequent charging. Check your tires monthly and keep them at the manufacturer’s recommended PSI to ensure the battery is working as efficiently as possible.
Using OBD-II Scanners
For the tech savvy owner, using an OBD-II scanner remains the best way to get “under the hood” of an EV. Apps like Torque Pro or dedicated EV tools can show you individual cell voltages. In 2026, look for “Cell Balance.” If one cell is significantly lower than the others, it could indicate a future failure. Modern BMS systems are good at balancing cells, but keeping an eye on this data once or twice a year provides peace of mind.
Seasonal Storage Tips
If you plan on leaving your EV unused for more than a week, 2026 storage protocols are very specific.
- Never store an EV at 100 percent or 0 percent charge.
- The ideal storage level is 50 percent.
- Store the vehicle in a cool, dry environment.
- Ensure the 12V or 16V auxiliary battery is also maintained, as a dead auxiliary battery can sometimes prevent the high voltage system from engaging.
Summary of 2026 Best Practices
To summarize the most effective ways to extend your EV battery life in 2026, follow this checklist:
- Keep the charge between 20 percent and 80 percent for daily NCM pack use.
- Charge LFP batteries to 100 percent once a week for calibration.
- Use Level 2 AC charging at home whenever possible.
- Precondition the battery before driving in extreme cold or heat.
- Install all over the air or OTA software updates promptly.
- Limit the use of ultra fast 350kW+ chargers to long trips.
- Maintain proper tire pressure to reduce motor strain.
- Park in the shade and stay plugged in during high heat.